
drawing: map of the eye drawn by the ophthalmologist G

Fįascia: any layer-like structure, usually tough and encircling anotherįit: the ability of the prosthesis to closely conform to the exact socket, usu by casting with the aid of an impressionįornix: the outermost extension of a pocket or socket, esp the farthest reaches of the conjunctival sacįovea: center of the macula, one degree of the sharpest visionįundus: the posterior of the eye as seen through an ophthalmoscope f. Coronal CTs containing the eyes and brain are viewed nose-up, from belowĬul-de-sac: any tissue pocket with only one exit Dĭelamination: separation of layers in the prosthesis, usu at the edges or limbusĭisc Diameter: horizontal measure of the optic nerve head (± 1-1.5 mm), used to measure distances in the fundus EĮctropion: outward turning of the eyelashesĮdema: swelling, retention of fluid from the lymphatic systemĮndothelium: any tissue lining the inside of a cavity in the bodyĮnophthalmos: inward malposition of the globe or orbital tissues due to a lack of volume, see superior sulcusĮntropion: inward turning of the eyelashesĮnucleation: surgical removal of the eye.Įpisclera: a thin layer of loose connective tissue nearest the scleraĮpithelium: tissue coving the outside of the body epithelialized: healing resulting in a keratinized covering of an otherwise endothelial areaĮquator: the portion of the eye most distant from either poleĮvisceration: surgical removal of the eye contents only, leaving the sclera and muscle insertions intactĮxeneration: surgical removal of all tissue in the orbitĮxopthalmos: forward malposition of orbital elements, bulging eyesĮxtraocular muscles (EOMs): any muscle moving the eyeĮxtrusion: portion of an implant exposed through a covering layerĮxudate: any substance excreted in reaction to stimulus or irritationĮyelid retractors: fascial extensions from the inferior rectus containing the lower lid Müller’s muscleĮyelid: skin-covered structure that protects the front of the eye. cretion: anything leaving a gland secretion, excretion, concretionĬryo-: freezing element c-therapy: freezing treatment for tumor(s) c-probe: freezing wand used to handle water-containing structures to be removed.ĬT (or CAT) scan: uses x-ray to show the body in sections.
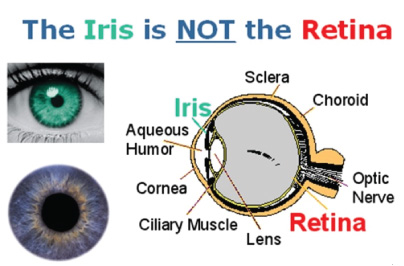
space, c.Ĭornea: clear outer part of the anterior eye, main focusing lensĬranial nerve: any of the ten nerves most central to the brain in the orbit, these are II (optic), III(oculomotor): supplies the medial, superior, inferior, an inferior oblique muscles IV(abducens): supplies superior oblique V1 (orbital trigeminal): frontal and inferior orbital sensory nerves VI(lacrimal): supplies the lateral rectus muscle remembered as LR6SO4, all the rest III Exits the eye through the limbus to enter the venous bloodstream.īiopsy: any removal of tissue for diagnostic evaluationīlepharoptosis: drooping of the upper lid due to deficient development or paralysis of the levator palpebrae muscle.īlowout fracture: an explosive event producing an out-fracture of thin orbital bone in any direction, can entrap EOMs and affect motilityīutton: any disc-like structure, esp the iris of a prosthesis CĬanthal tendon: any tendon of the pretarsal orbicularis oculi muscle inserting into boneĬanthus: either corner of the palpebral fissure medial c.: nasal corner lateral c.: temporal corner of the eyelidsĬaruncle: a specialized extension of the conjunctival mucosa at the nasal canthus adjacent fold of mucosa is the plica semilunarisĬast: hardening a positive copy in a moldĬentral retinal artery: the artery entering the eye with the optic nerve to supply the anterior layers of the retinaĬhoroid: layer of blood vessels feeding the posterior retina.Ĭollarette: ring in the colored iris usually about halfway from the pupil, representing the widest dilation of the sphincterĬoloboma: a cleft, usu in the iris or retinaĬonformer: a smooth spacing element inserted at surgery to support the eyelids and retain socket dimensions while healingĬongenital: anything present at or from birthĬonjunctiva: mucous membrane that protects the eye (bulbar c.) and lids (palpebral c.) in an anophthalmic socket, this membrane lines the socket and covers the implant.Ĭonjunctiva: c. Anterior chamber: front-most portion of the eye containing all structures bathed in aqueous humor: cornea, iris and limbus, lens, ciliary bodiesĪqueous humor: watery fluid secreted from the ciliary bodies and ciliary processes that acts like the blood for the anterior chamber structures and cornea.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
